BFcache: Speed Up Back and Forward Navigation
Back/forward cache (BFcache) is a browser optimization that enables instant back and forward navigation. It significantly improves browsing, especially for users on slow networks or devices.
What Is BFcache
BFcache stores a full snapshot of a page in memory when the user leaves it. Because the entire page is cached—including JavaScript—the browser can instantly restore it without repeating network requests.
This video shows how much BFcache accelerates navigation:
Addy Osmani: BFcache on Chrome for Android
How BFcache Works
Unlike HTTP cache, which only stores responses to individual requests, BFcache keeps a full in-memory snapshot of the page, including its JavaScript state. Restoring from BFcache is always faster than even the best-optimized load without it—effectively showing the previous page state instantly.
:::tip You can track BFcache usage with Navigation Types in our Monitoring PLUS. :::
Browser Support
BFcache has been supported for years in Firefox and Safari on both desktop and mobile.
Chrome started enabling BFcache on Android for a small percentage of users in version 86, and rolled it out to all desktop and mobile users in version 96.
The Chrome team noted: “BFcache brought the biggest CLS improvement we saw in 2022.”
Optimizing for BFcache
Not all pages are eligible for BFcache, and even cached pages don’t stay forever. Developers should aim to maximize the number of pages that qualify.
Event unload
Use the pagehide event instead of unload. Never attach unload listeners—this is the single most important step for BFcache compatibility. Also ensure no third-party scripts use it.
Check with the no-unload-listeners audit in Lighthouse.
 Unload event audit in Lighthouse
Unload event audit in Lighthouse
Cache-Control: no-store
Avoid Cache-Control: no-store. Prefer no-cache or max-age=0.
- Use
no-storeonly for sensitive, logged-in content. - For non-sensitive pages that should always refresh, use
no-cacheormax-age=0. These still allow BFcache while forcing revalidation.
 Using
Using Cache-Control: no-cache keeps pages eligible for BFcache.
Window.opener
Avoid window.opener.
Old links with target=_blank but without rel="noopener" created an opener reference, preventing safe BFcache storage and adding security risks.
Always use rel="noopener"—modern browsers apply this by default.
Open Connections
Close all open connections before the user leaves, including:
IndexedDBsessions- Ongoing
fetch()orXMLHttpRequest WebSocketorWebRTCconnections
👉 For more, see this Chrome Developers video on debugging and optimizing for BFcache.
Testing BFcache
How to check if your pages load from BFcache:
DevTools
- Open your page in Chrome.
- In DevTools, go to Application > Back/Forward cache.
- Click Run Test to see the page’s BFcache status.
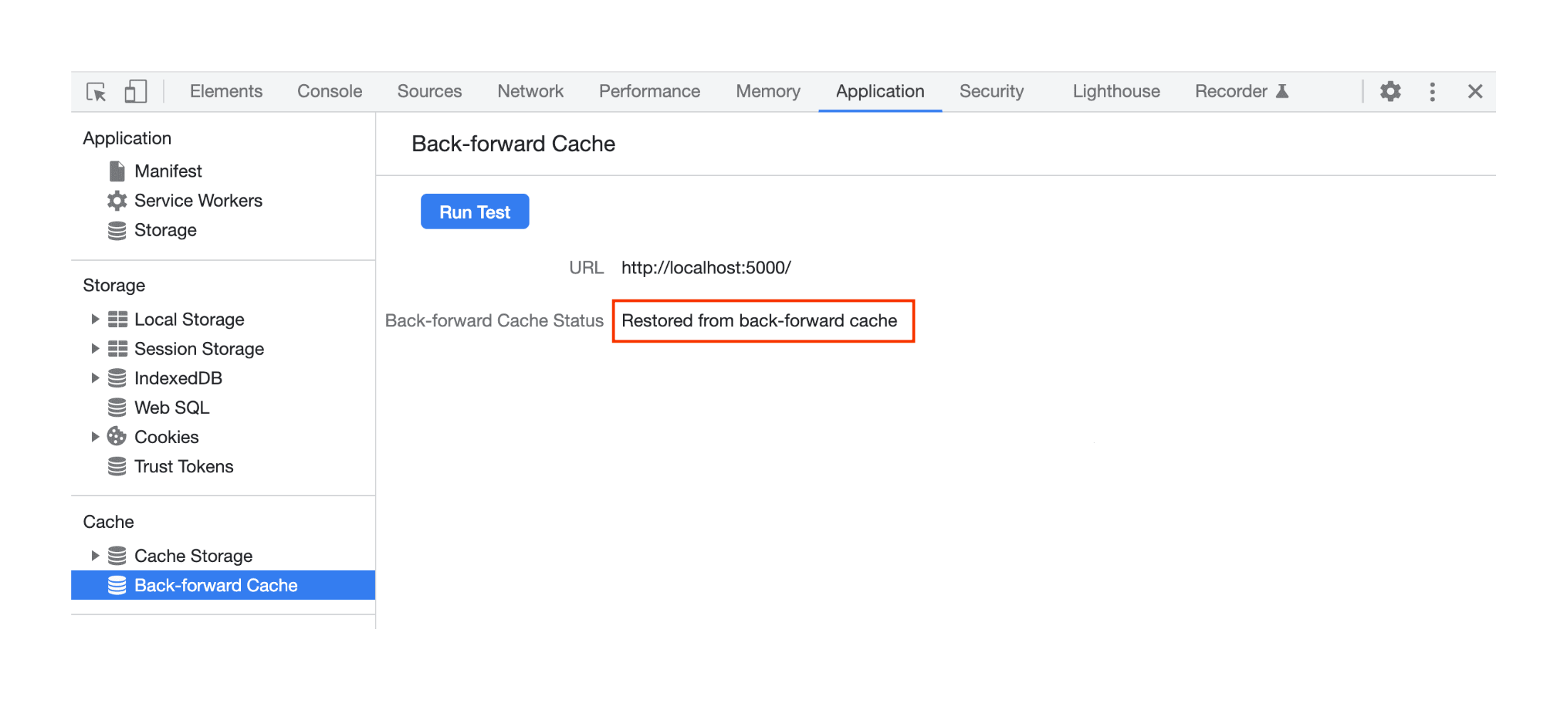 A page stored in BFcache.
A page stored in BFcache.
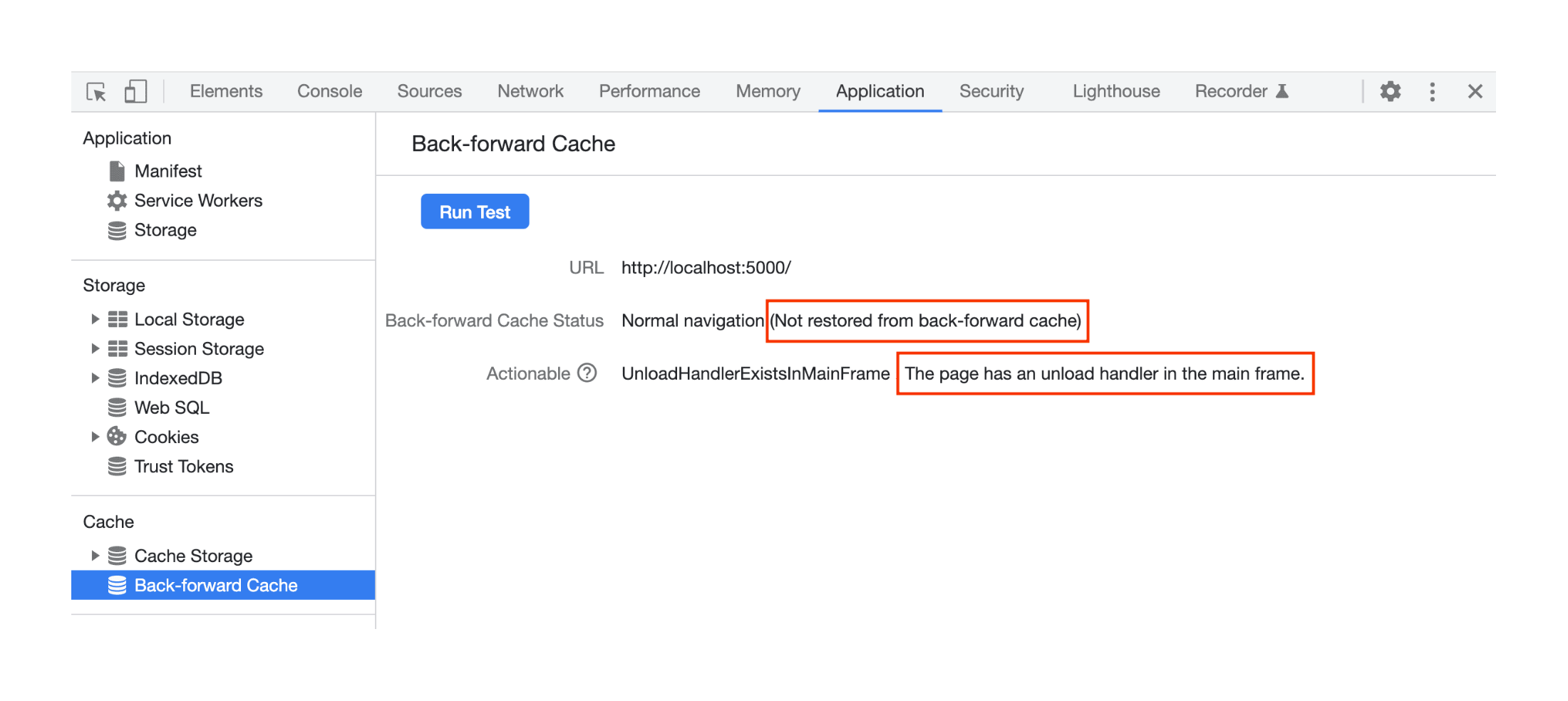 A page not stored in BFcache.
A page not stored in BFcache.
Lighthouse 10
Lighthouse audits also test BFcache eligibility.
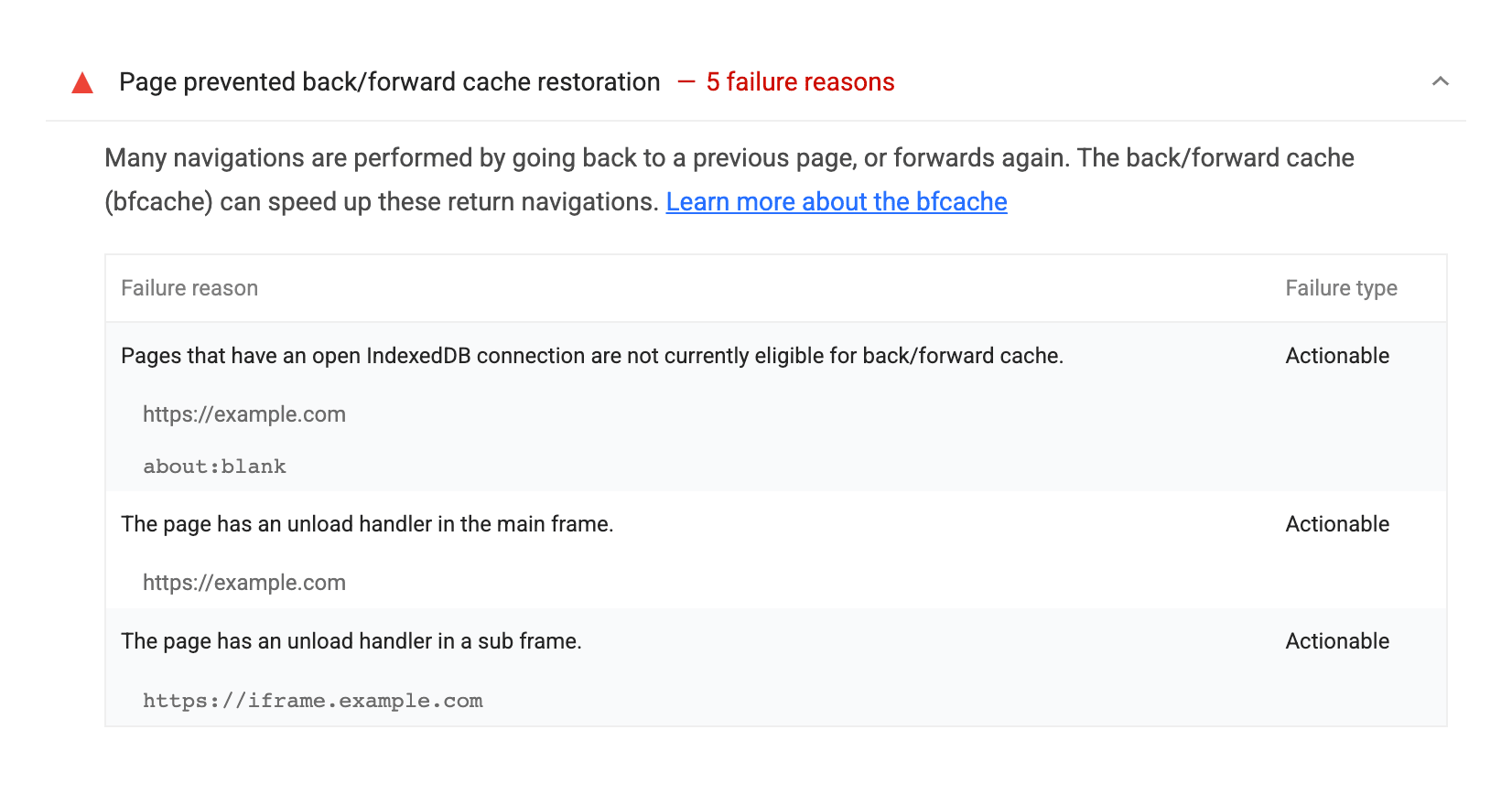 Lighthouse 10
Lighthouse 10
Drawbacks
While BFcache improves speed and smoothness, there are trade-offs:
Memory Use
Storing full page states consumes memory, especially on mobile or older devices.
Possible Data Inconsistency
Interactive features like forms, carts, or chat windows may show outdated data if BFcache is not properly handled.
Security Risks
Caching sensitive content can expose it on shared or unsecured devices. Handle logged-in pages with care.
Despite these, BFcache generally improves performance and user experience.
Impact on Core Web Vitals
BFcache strongly affects Core Web Vitals:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) BFcache speeds up LCP by instantly restoring primary content on back/forward navigation.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) BFcache helps reduce unexpected shifts compared to full reloads.
Interaction to Next Paint (INP) and First Input Delay (FID) BFcache can lower input delays since no fresh load or render is needed.
We covered BFcache in our recent webinar:
Enable BFcache
By removing blockers, you gain:
- Faster navigation Pages restore instantly on back/forward, boosting user experience.
- Lower data usage BFcache reduces redundant requests and rendering.
- Better UX and Core Web Vitals Faster loads and smoother navigation improve satisfaction and key metrics.